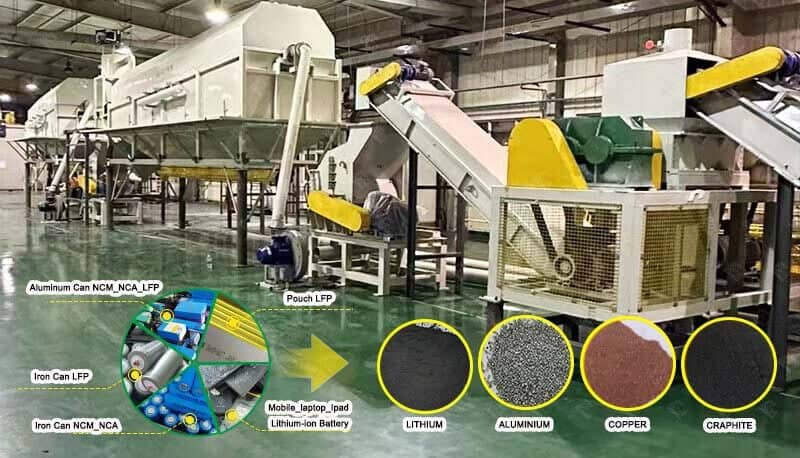
In the evolving landscape of battery recycling, the battery black mass recycling process stands out as a pivotal technique for recovering valuable metals. This article aims to demystify the process, highlighting its significance and benefits within the circular economy framework.
Battery black mass refers to the powdery residue obtained after the mechanical shredding of spent batteries. It primarily contains a mix of valuable metals like lithium, cobalt, nickel, and manganese, along with other components. The battery black mass recycling process focuses on extracting these metals efficiently and sustainably.
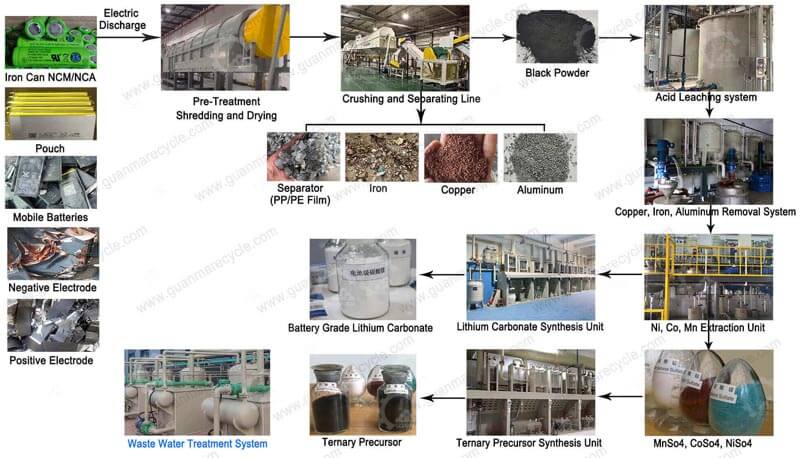

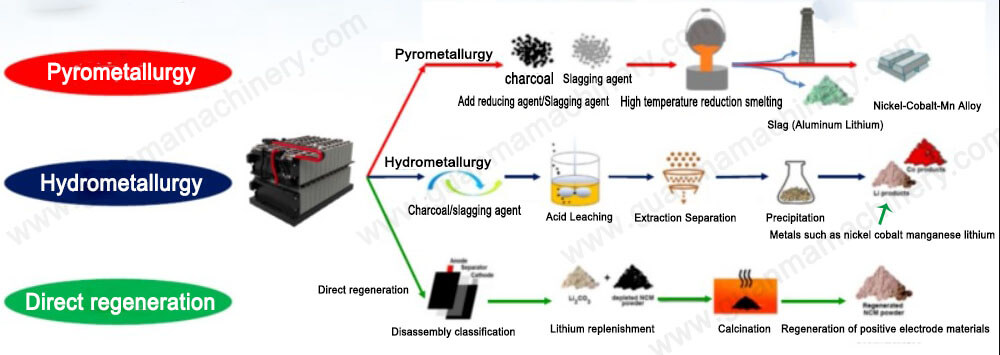
The battery black mass recycling typically involves several stages:
1. Pre-Treatment: Spent batteries undergo shredding and sorting to remove non-metallic parts and produce black mass.
2. Leaching: The black mass is treated with chemical solutions to dissolve the metals. This step separates the valuable metals from impurities.
3. Extraction and Purification: Further processes, such as solvent extraction or precipitation, refine the dissolved metals to higher purity levels.
4. Metal Recovery: The purified metals are then processed to produce high-quality metal compounds or alloys, ready for reuse in new batteries or other applications.
The battery black mass recycling process offers several advantages:
1. Resource Conservation: It reduces the need for virgin raw materials, conserving natural resources and decreasing the environmental impact of mining.
2. Economic Viability: The recovery of high-value metals contributes to the economic feasibility of recycling, potentially lowering the overall cost of battery production.
3. Environmental Protection: By preventing the disposal of toxic battery components, this process minimizes pollution and promotes a safer environment.