Lithium Battery Recycling Technologies
The recycling process for spent lithium-ion batteries primarily involves three methods: Physical Separation, Pyrometallurgy (fire method), and Hydrometallurgy (wet method).
Types of Lithium-ion Batteries
Depending on the equipment and applications they are used in, lithium-ion batteries come in various shapes such as cylindrical, prismatic, or pouch cells. However, all types generally consist of five main components: the cathode, anode, electrolyte, organic separator, and casing.
Main Components of Lithium Batteries
Casing: Made from materials like stainless steel, nickel-coated steel, or aluminum.
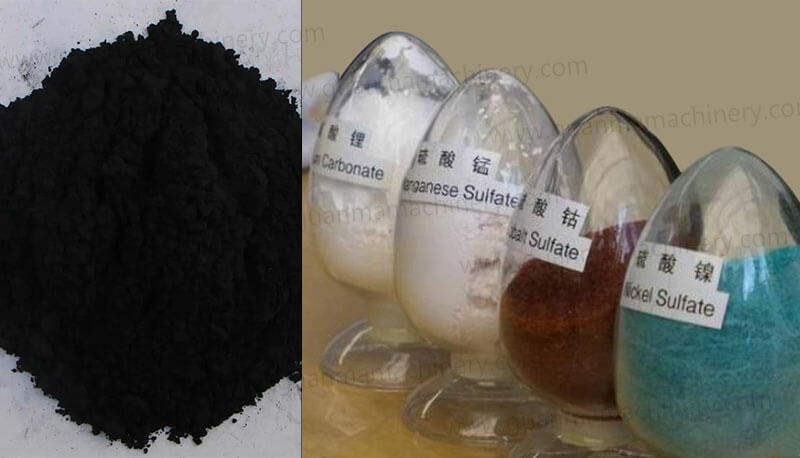
Cathode: Comprises active materials (such as NCM, LFP), conductive agents, and binders; with aluminum foil serving as the current collector.
Anode: Consists mainly of active substances (like graphite, lithium titanate), conductive agents, and binders; copper foil is predominantly used as the current collector.
Electrolyte: Primarily consists of a lithium salt electrolyte and organic solvents with additives.
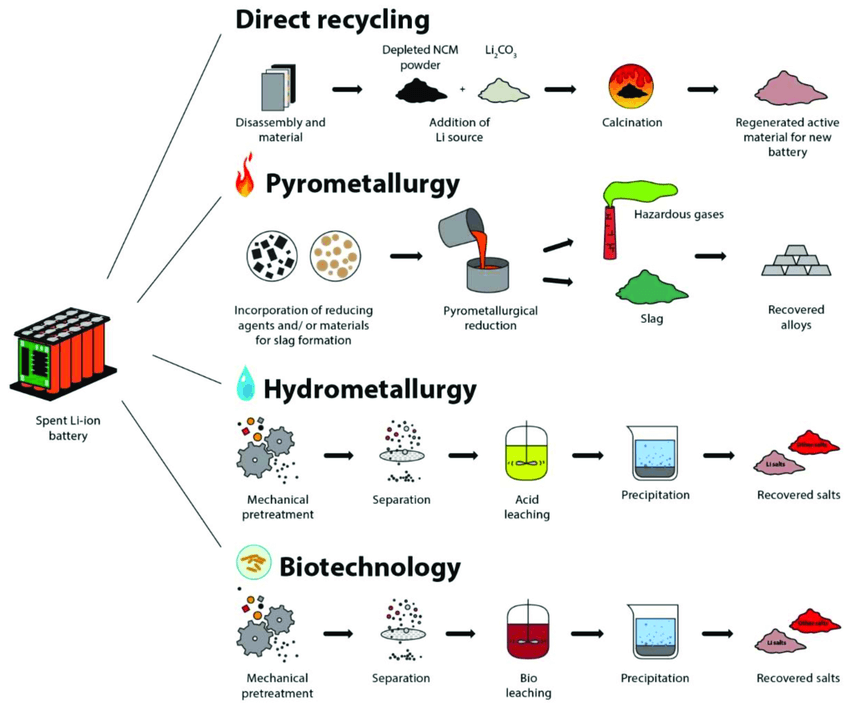
Why Recycle Spent Lithium Batteries?
Pollution Prevention: Spent lithium-ion batteries contain metals in their cathodes, carbon dust from anodes, and strong alkalis and heavy metals in the electrolytes, all of which can cause significant environmental pollution if not properly handled.
Resource Recovery: Discarded lithium-ion batteries contain valuable metals (such as cobalt, lithium, nickel, etc.), making recycling economically beneficial.
Lithium Battery Recycling Technologies—Physical Separation, Pyrometallurgy, and Hydrometallurgy—are common approaches to recycling lithium-ion batteries. For more information on recycling processes including physical separation, pyrometallurgical, and hydrometallurgical methods for spent lithium-ion batteries, feel free to reach out to us!





