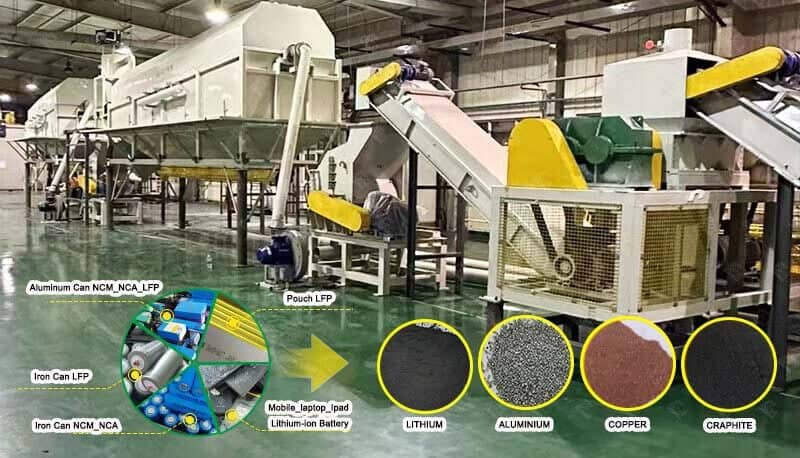
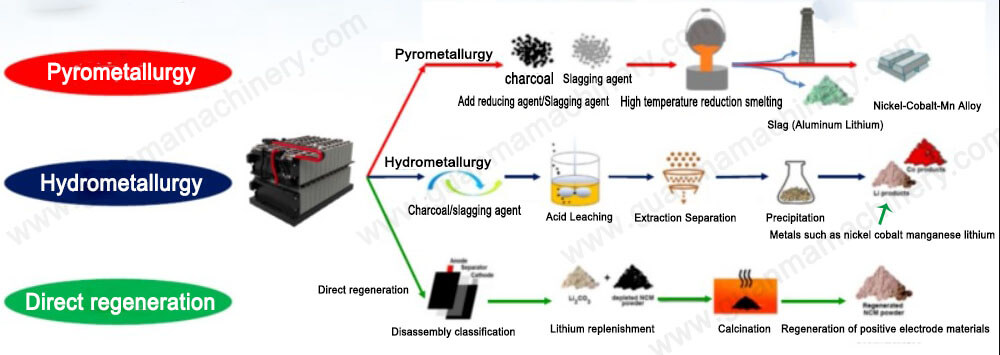
The electrode reactions in the copper electrolytic refining process involve using pure copper sheets as the cathode and an anode made of copper plates that contain minor impurities (typically 0.3% to 1.5%). The electrolyte is primarily a solution of copper sulfate with free sulfuric acid.
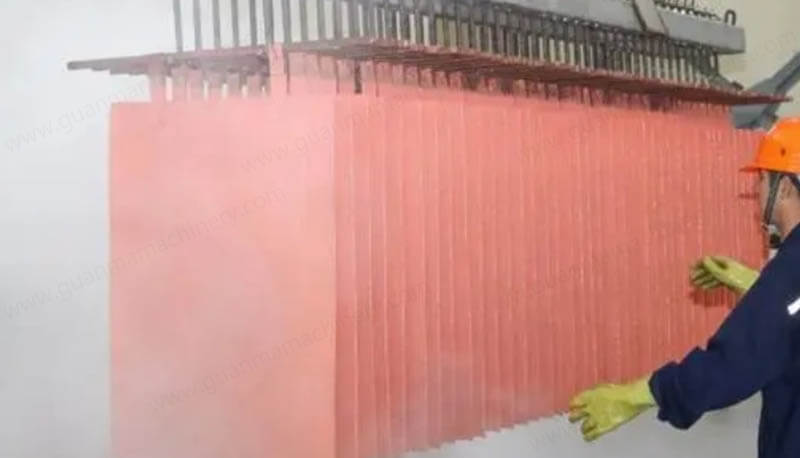

Due to ionization, the components of the electrolyte form ions according to the following reactions. When no current is applied, the following reactions are in dynamic equilibrium. Upon applying an electric current, the electrolyte is fully or partially ionized:
CuSO₄ = Cu²⁺ + SO₄²⁻
H₂SO₄ =2H⁺ + SO₄²⁻
H₂O =H⁺ + OH⁻
The various ions undergo directed movement; cations move toward the cathode, while anions move toward the anode. Simultaneously, electrochemical reactions occur at the interfaces between the electrodes and the electrolyte.