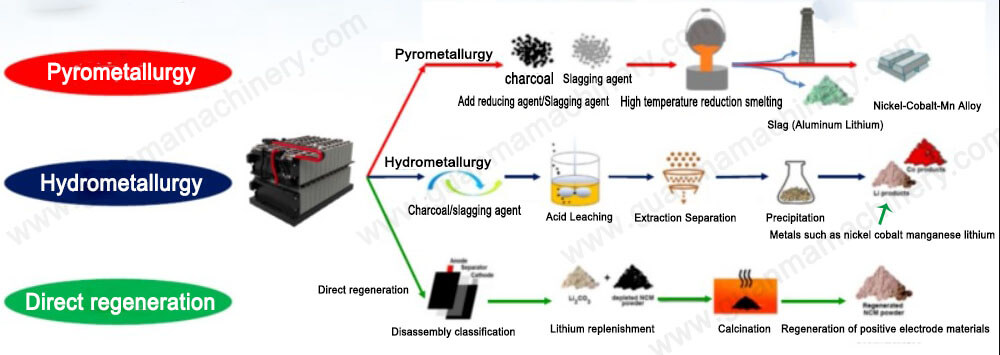
Battery recycling processes can generally be categorized into three major types based on extraction methodologies: hydrometallurgical recovery technology, pyrometallurgical recovery technology, and physical shredding recovery technology. Currently, hydrometallurgical recovery technology dominates the dismantling and regeneration recycling methods.
Why recycle batteries?
With the escalating penetration rate of new energy vehicles, the demand for power lithium-ion batteries is rapidly increasing. When a power battery’s capacity fades to below 80%, there is a noticeable decline in its electrochemical performance, making it insufficient for the standard power requirements of automobiles, thus entering the routine replacement phase. Given the typical lifespan of around five years, new energy vehicles will face battery replacement demands in the coming years, potentially generating hundreds of thousands of tons of spent lithium-ion batteries.
Heavy metals contained in spent power batteries pose significant threats to the ecological environment. If disposed of through conventional waste management methods like landfilling or incineration, environmental pollution is inevitable. Therefore, the recycling of replaced lithium-ion batteries is of paramount importance. Valuable metals such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel extracted from spent lithium-ion batteries yield considerable resource value. After extracting valuable metals and materials, they can be reintroduced into the production of battery cells, modules, and systems, forming a closed-loop throughout the entire life cycle of lithium-ion batteries.
When battery capacity drops below 20%, the batteries are disassembled for material recovery. During the disassembly process, heavy metals including nickel, cobalt, lithium, and manganese can be retrieved. The rising prices of precious metals and the scarcity of mineral resources highlight the value of recycling spent lithium-ion batteries. Recycling is efficient and, compared to direct mining operations, presents a cost advantage due to higher recovery rates and lower energy consumption.

Hydrometallurgical methods
Hydrometallurgy primarily involves chemical/electrochemical and bioleaching reactions to transfer valuable metals from electrode materials into the liquid phase. Subsequently, these valuable metals are separated and concentrated in the liquid phase before being recovered in the form of metals or other compounds. Key methods for the separation and purification of valuable metals include ion exchange, extraction, precipitation, and electrochemical deposition.
Hydrometallurgical recovery methods are characterized by high recovery rates, high product purity, and low energy consumption, making them a preferred choice in the recycling industry.