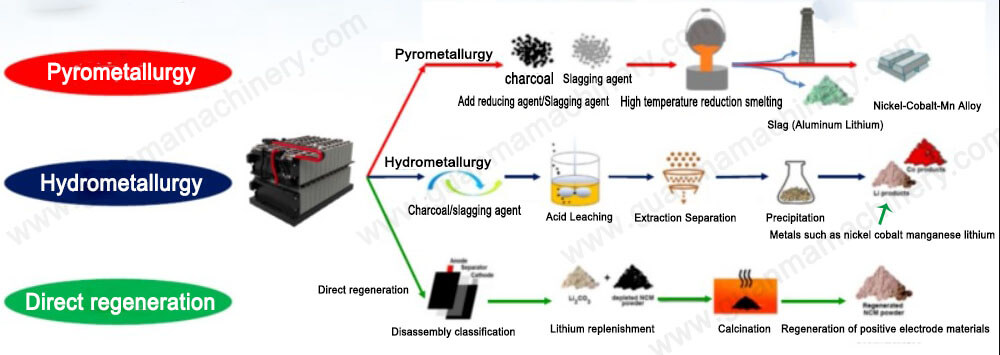
In the world of sustainable technology, recycling used batteries is a major concern. The processes of hydrometallurgy and pyrometallurgy are two of the most prominent methods used for extracting valuable materials from old batteries. But what exactly are these techniques, and how do they compare when it comes to recycling batteries efficiently?
Hydrometallurgy vs Pyrometallurgy:
Hydrometallurgy involves using aqueous solutions to extract metals, while pyrometallurgy relies on high temperatures to break down materials. Both methods have their unique advantages and challenges in battery recycling. Hydrometallurgy is often seen as a more environmentally friendly choice because it requires lower energy input and is better at selectively extracting precious metals like cobalt, nickel, and lithium. On the other hand, pyrometallurgy is effective in processing large quantities of batteries and can recover a broader range of metals, though it typically requires more energy and may result in higher emissions.
Which is Best for Battery Recycling?
The choice between hydrometallurgy vs pyrometallurgy largely depends on factors such as the type of batteries being recycled, the efficiency of the methods, environmental considerations, and cost. While hydrometallurgy is ideal for battery types that contain high amounts of precious metals, pyrometallurgy may still be more suitable for large-scale operations or mixed types of battery waste. Each method offers a different balance of environmental impact and recovery rates, and the best solution may often lie in a combination of both.
Conclusion:
As the demand for electric vehicles and renewable energy solutions grows, improving battery recycling technologies becomes more crucial. Understanding the differences between hydrometallurgy vs pyrometallurgy can help guide the future of battery recycling in a more sustainable direction.