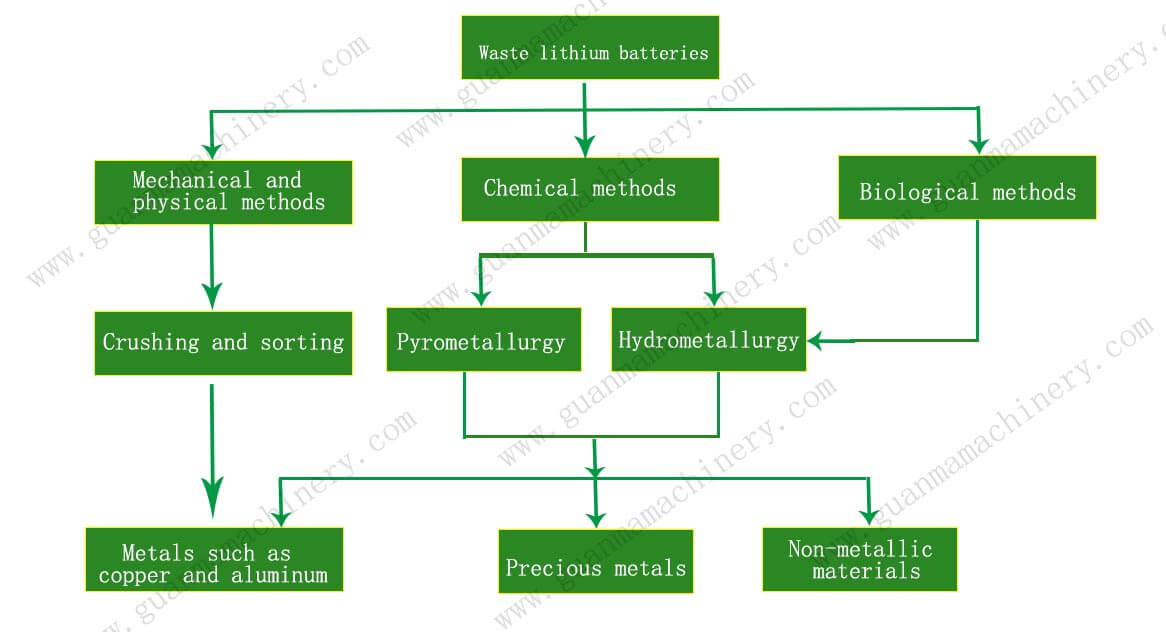
With the widespread application of lithium-ion batteries across various fields, the number of spent batteries is also on the rise. Effective recycling of these batteries not only minimizes resource wastage but also reduces potential environmental harm. Let’s delve into the details of lithium-ion battery recycling processes.
Pre-Processing of Lithium-Ion Batteries
The recycling process begins with pre-processing, which includes collecting, sorting, and disassembling the spent batteries. Collected batteries must be carefully classified based on their type and specifications to determine the most appropriate recycling method. The disassembly process requires meticulous handling to prevent leakage of internal contents and protect the handlers.
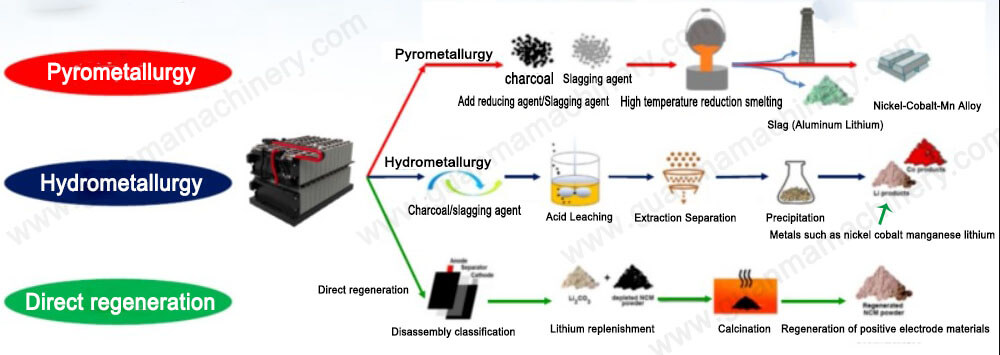
Extraction of Valuable Metals
Lithium-ion batteries contain a range of valuable metals, including cobalt, nickel, and lithium. Common extraction methods include pyrometallurgy and hydrometallurgy.
Pyrometallurgy
Pyrometallurgy involves high-temperature smelting to convert the metallic elements within the batteries into metallic solids or alloys. This method is relatively simple in terms of process, but it consumes a significant amount of energy and may generate gases and residues that need to be managed properly.
Hydrometallurgy
Hydrometallurgy utilizes chemical reagents to dissolve metals, followed by a series of chemical reactions and separation processes to extract target metals. This method boasts higher metal recovery rates and purities, with a smaller environmental impact, although the process is more complex.