Do You Know the Four Common Methods for Recycling Lithium Iron Phosphate Batteries?
Lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries were among the earliest lithium-ion batteries used in power applications and are the most widely utilized in energy storage systems. Spent LFP batteries are the main targets for lithium-ion battery recycling.Conventional pyrometallurgy, hydrometallurgy, and the combined use of both are mature techniques and currently dominate the recycling scene. Meanwhile, the restoration regeneration method and the eutectic solvent leaching method are emerging approaches offering distinct advantages in terms of economics and environmental friendliness.
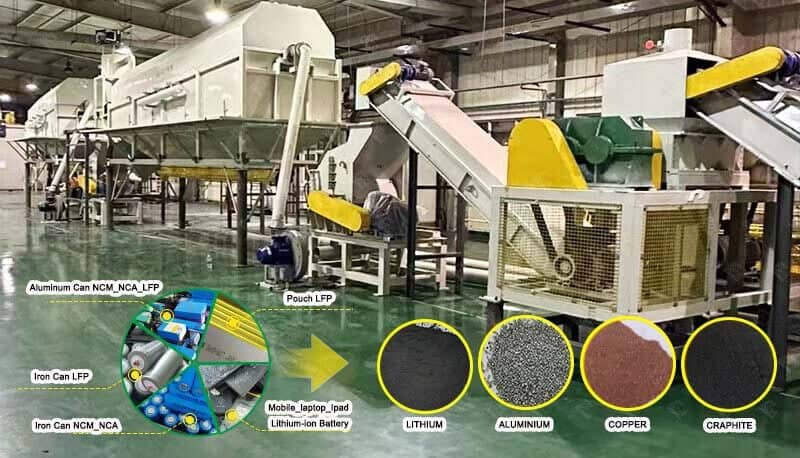
The main focus of lithium-ion battery recycling is on the economically valuable cathode materials, which after being crushed, undergo a series of physical and chemical treatments to recover lithium, nickel, cobalt, and other metals in the form of oxides or salts. Since LFP does not contain cobalt or nickel, and iron has limited standalone recycling value, the primary target for recycling is lithium salts. The residual iron and phosphorus are co-recycled as precursors in the form of ferric phosphate.

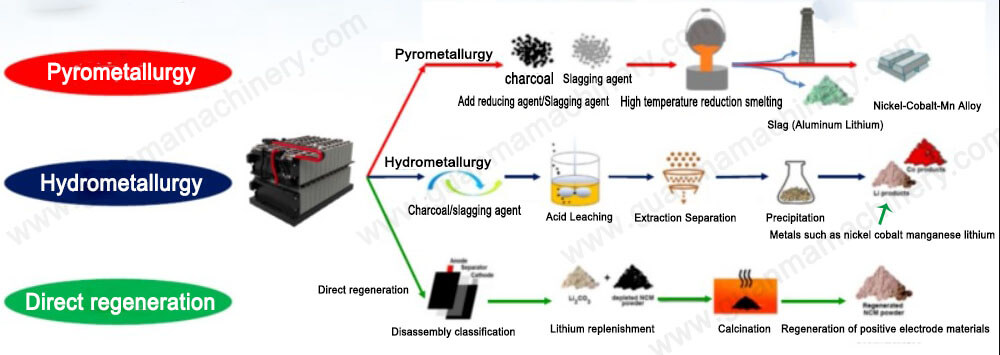
Main methods of battery recycling
Currently, the dominant recycling methods are pyrometallurgy, hydrometallurgy, and the hybrid pyro-hydrometallurgical approach.
1. Pyrometallurgy: This involves high-temperature incineration to burn off organics within the battery, with valuable metals forming oxides that can be slagged and purified. However, this method is energy-intensive and has low efficiency in separating mixed metals.
2. Hydrometallurgy: Primarily uses acid-base leaching to extract valuable metals from the cathode materials. To increase efficiency, acids and bases are often used in excess, leading to substantial volumes of acid-base wastewater, which increases the environmental cost of post-treatment.
3. Restoration Regeneration Method: This method restores the electrochemical performance of degraded cathode materials through lithium supplementation and high-temperature activation. It features a simple process flow, short production cycle, and higher economic benefits.
4. Eutectic Solvent Leaching Method: At low temperatures, spent LFP cathode materials react chemically with eutectic solvents to leach valuable metals, which are subsequently separated and purified. This method avoids the use of inorganic acids and bases, produces no exhaust gases, requires minimal equipment space, and has a straightforward reaction process.