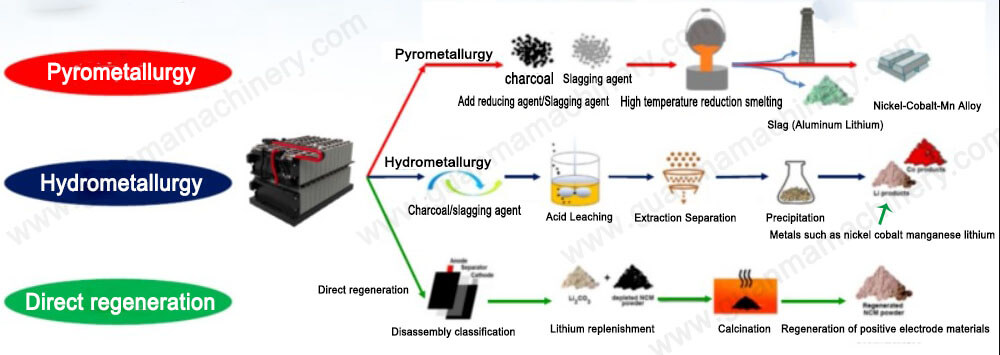
Hydrometallurgy of Lithium-Ion Batteries
Hydrometallurgy refers to a method of extracting metals from their ores using aqueous (water-based) solutions. In the context of lithium-ion batteries (LIBs), hydrometallurgy is a technique used to recover valuable materials—such as lithium, cobalt, nickel, and other metals—from spent or discarded lithium-ion batteries through chemical processes involving water or aqueous solutions.
Process Overview of Hydrometallurgy in LIB Recycling
The hydrometallurgical process for recycling lithium-ion batteries typically involves several key steps:
Pre-Treatment (Mechanical and Thermal Processing)
The first step is to remove the casing and other non-metallic components from the battery. This can be done through mechanical processes like crushing and shredding. The battery is then subjected to thermal treatment (often referred to as pyrolysis) to break down organic materials like plastics, electrolyte, and other impurities. This step also helps stabilize the metal-rich residues for further processing.
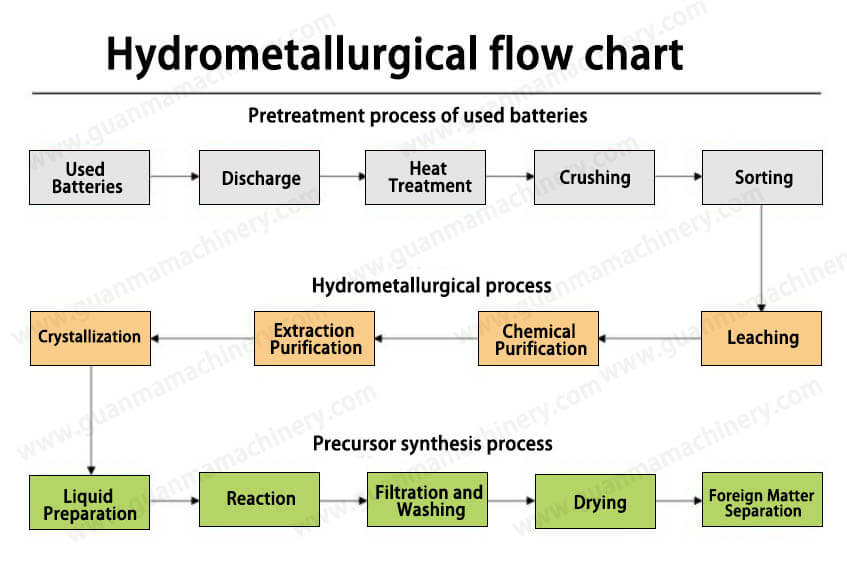
Leaching
In the leaching process, the metal-containing residue (often from the cathode and anode materials) is mixed with an acidic or basic aqueous solution. Common chemicals used for leaching include sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄), nitric acid (HNO₃), or a combination of acids and bases. The goal is to dissolve valuable metals like lithium, cobalt, and nickel into the solution. This step is crucial because it separates the metals from the solid residue and makes them available for further extraction.
Solvent Extraction
After leaching, the solution typically contains a mix of metals. Solvent extraction is used to selectively separate these metals from one another. By adding specific organic solvents, certain metals can be extracted into a separate phase (usually a liquid), leaving behind other unwanted substances. This separation process can be repeated multiple times to purify the metals.
Precipitation and Purification
Once the metals are separated, they may need to undergo precipitation. This involves adding chemicals to the solution that cause specific metals to form solid compounds, which can then be filtered out. This process helps to further purify the metals, ensuring that the extracted lithium, cobalt, nickel, and other materials are of high purity.
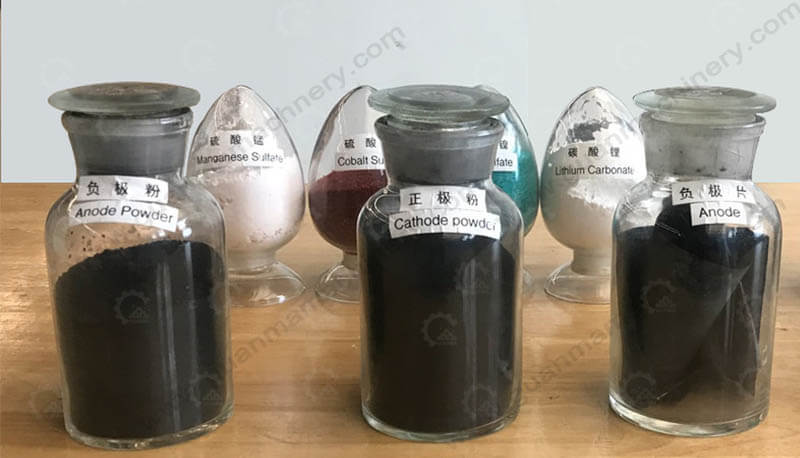

Recovery and Refining
Finally, the metals obtained from the leaching and precipitation steps are refined into their pure metallic form through additional chemical reactions, such as electrolysis. The refined metals are then ready to be reused in new batteries or other industrial applications.
Advantages of Hydrometallurgy for Recycling LIBs
Efficient Metal Recovery: Hydrometallurgy allows for the efficient recovery of critical materials like lithium, cobalt, nickel, and manganese, which are often in high demand for battery production.
Environmental Benefits: It is generally considered more environmentally friendly compared to traditional smelting processes because it uses less energy and results in fewer emissions.
Selective Recovery: Hydrometallurgy can selectively recover specific metals, which is important as lithium-ion batteries contain a mix of valuable and less valuable metals.
Hydrometallurgy is a promising and increasingly popular method for recycling lithium-ion batteries, allowing for the recovery of valuable metals like lithium, cobalt, and nickel.