Gold electrolysis is a process used to extract gold from its ores or refine gold to a higher purity. The process involves the use of an electrolyte solution and an electric current to separate gold from other materials. Here’s an overview of the gold electrolysis process:
Gold Electrolysis Process
1. Preparation of the Electrolyte Solution
The electrolyte solution is typically made using a mixture of gold chloride (AuCl₃) or gold cyanide (NaAu(CN)₂) dissolved in water. The gold chloride solution is often preferred for gold electrorefining.
2. Setting Up the Electrolytic Cell
The electrolysis cell consists of two main components:
Anode: This is where the impure gold (usually in the form of gold bars or gold-containing material) is placed.
Cathode: A sheet of pure gold is placed here, which will collect the refined gold as it is deposited.
Both the anode and cathode are immersed in the electrolyte solution.
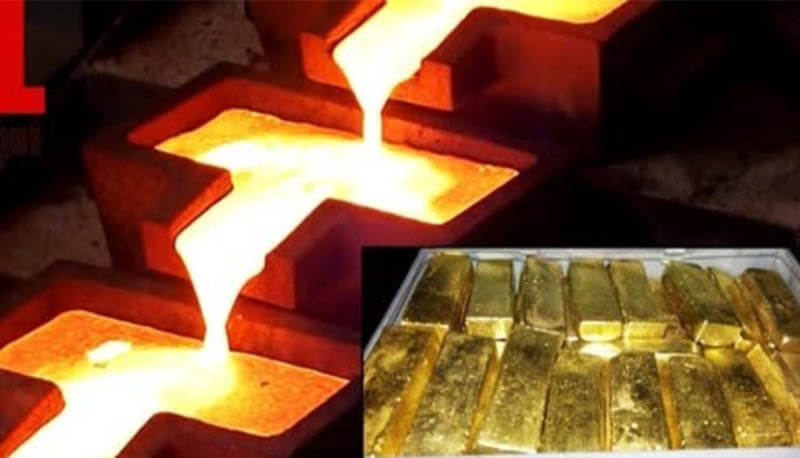

3. Applying Electric Current
An electric current is passed through the electrolyte solution. The process causes gold to dissolve from the anode (impure gold) and be deposited onto the cathode (pure gold).
4. Electrolysis Reaction
The main electrochemical reaction in the process is:
At the anode (impure gold): Gold dissolves into the electrolyte as gold ions
At the cathode (pure gold): Gold ions (Au³⁺) from the electrolyte are reduced and deposited onto the cathode.
5. Refining the Gold
As the electrolysis continues, pure gold builds up on the cathode, while impurities such as silver, copper, and other metals remain in the electrolyte or are left behind at the anode as slimes.
6. Final Steps
Once the electrolysis process is complete, the gold that has been deposited on the cathode is removed, cleaned, and melted to form gold bars or other forms of refined gold.
The impurities in the electrolyte can be further processed or discarded, depending on the specific materials.
Advantages of Gold Electrolysis:
High purity: Electrolysis can produce gold with purity levels of 99.99% or higher.
Precision: Electrolytic refining allows for precise separation of gold from impurities.
This process is widely used for both the extraction of gold from ores and the refinement of gold to a high purity.