In the realm of industrial recycling, lead recycling plants stand out as vital facilities for environmental conservation and resource recovery. Lead, a dense and highly versatile metal, is widely used in batteries, ammunition, radiation shielding, and alloys. However, its toxicity necessitates careful handling and recycling.
Understanding Lead Recycling Plants
A lead recycling plant is a specialized facility designed to reclaim and process spent lead-acid batteries, scrap lead, and other lead-containing products. The primary objective is to recover lead, which can then be reused in the manufacture of new batteries and other applications, thereby reducing the need for virgin lead mining and its associated environmental impacts.
The Recycling Process
The process of lead recycling typically involves several stages:
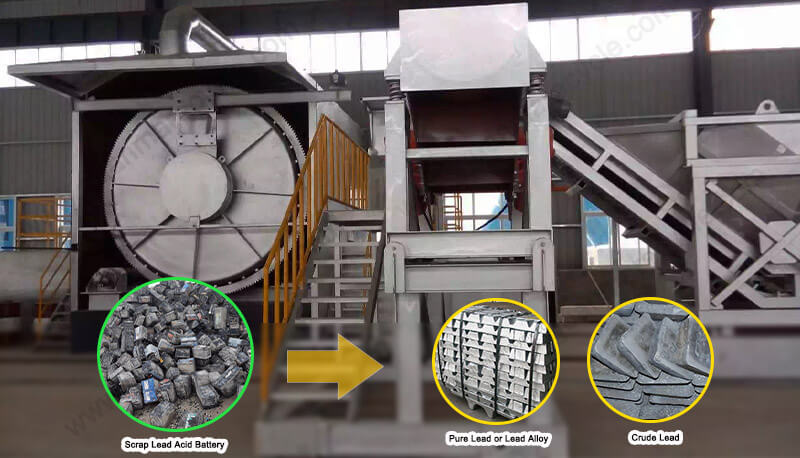
1. Collection and Sorting: Spent batteries are collected from various sources and transported to the recycling plant. Upon arrival, they are sorted to ensure compatibility with the recycling process.
2. Crushing and Separation: The batteries are mechanically crushed to break them down, allowing for the separation of lead components from plastics and electrolytes. This step often involves the use of water to separate lighter materials from heavier lead fragments.
3. Lead Recovery: The lead is then subjected to a series of treatments, including smelting, to remove impurities and refine it back to its elemental form. Smelting occurs in furnaces where the lead melts at high temperatures, separating from other materials.
4. EPA Compliance and Pollution Control: Stringent environmental controls are in place to manage emissions and ensure compliance with EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) regulations. This includes the use of filters to capture lead dust and gases.
Benefits of Lead Recycling
1. Resource Conservation: Recycling lead significantly reduces the demand for new mining activities, preserving natural resources and decreasing the environmental footprint associated with virgin lead extraction.
2. Energy Efficiency: The process of recycling lead requires less energy compared to producing new lead from raw materials. This translates to lower carbon emissions and energy consumption.
3. Economic Advantages: The sale of recycled lead generates revenue for recycling facilities, while also providing a cost-effective source of lead for manufacturers.
4. Job Creation: Lead recycling plants create employment opportunities in areas such as plant operation, maintenance, and administration.

Considerations When Setting Up a Lead Recycling Plant
1. Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to local, state, and federal environmental regulations is paramount. This includes obtaining necessary permits and maintaining continuous compliance with air and water quality standards.
2. Health and Safety Measures: Implementing robust health and safety protocols is essential to protect workers from exposure to lead and other hazardous materials.
3. Investment and Costs: Establishing a lead recycling plant requires significant capital investment, covering equipment, infrastructure, and operational costs. Evaluating the economic feasibility and potential return on investment is crucial.
4. Technology and Equipment: Choosing the right technology and equipment is key to efficient and effective lead recycling. This includes crushers, separators, smelters, and pollution control devices.
In conclusion, lead recycling plants play a critical role in the circular economy, offering environmental, economic, and social benefits. For businesses considering entry into this sector, understanding the process, benefits, and challenges is fundamental to success. By prioritizing sustainability and regulatory compliance, lead recycling can be a profitable and responsible venture.




